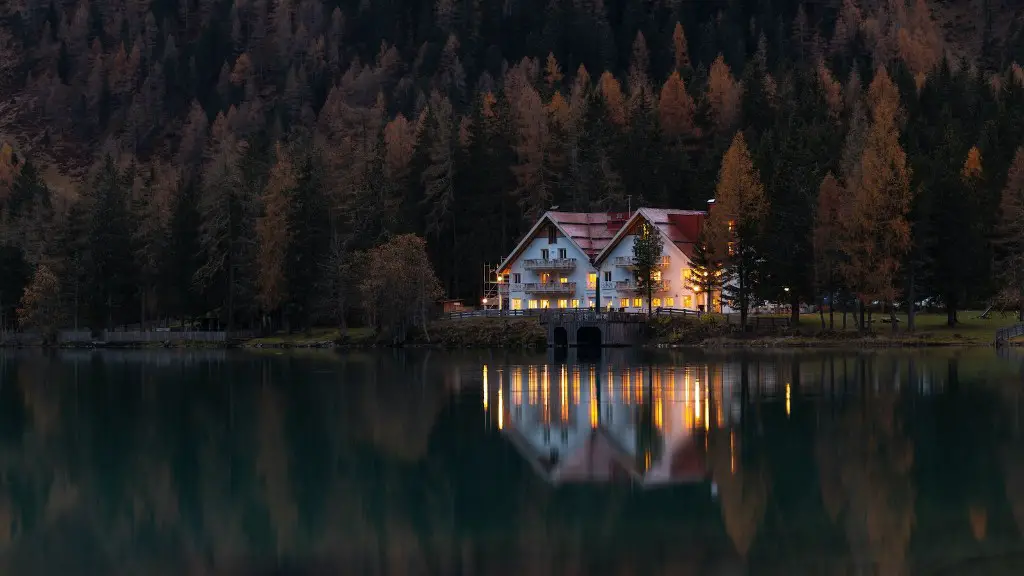
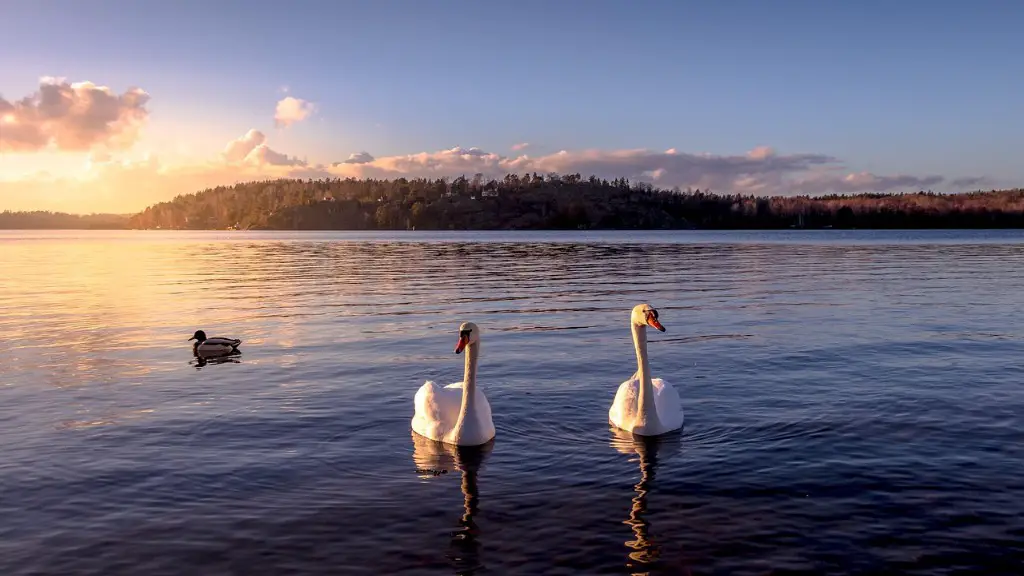Crater Lake National Park is home to a diverse array of trees, including conifers, hardwoods, and flowering plants. The most common trees are Douglas fir, western hemlock, whitebark pine, and lodgepole pine. The park also has an abundant amount of old-growth forests, which provide critical habitat for many animals and plants.
The trees at Crater Lake are Douglas fir, mountain hemlock, whitebark pine, and subalpine fir.
What plants and trees are in Crater Lake National Park?
The park is home to a variety of different vegetation types, from mixed conifer forests dominated by ponderosa pine in the south, to high-elevation mountain hemlock and whitebark pine forests at the rim. The park is a sanctuary for native forest and meadow communities, and in the lake itself, you’ll find layers of aquatic moss.
This is an amazing discovery because it shows that life can find a way to survive even in the most extreme conditions. The bottom of Crater Lake is a very hostile environment with almost no nutrients, yet these colonies of moss and bacteria are thriving. This just goes to show that life is very resilient and can find a way to survive even in the most challenging conditions.
Why is Crater Lake so blue
Crater Lake is one of the most beautiful and clear lakes in the world. Its vibrant blue color is a result of its depth and the lack of any sediment or mineral deposits. This makes it a great place to enjoy the views and take in the fresh air.
Pinus resinosa, also known as red pine, is a species of evergreen coniferous tree in the family Pinaceae. The tree is native to North America, where it occurs in the northern United States and southern Canada. It is a medium-sized tree, growing to 25-50 ft (75-15 m) tall and with a stout trunk up to 2 ft (60 cm) in diameter. The branches are spreading, sometimes pendulous, and form a broad, pyramidal head. The bark is red-brown, shallowly fissured and scaly. The needles are in bundles of two, flexible, 12-17 cm long, and blue-green to yellow-green in color. The cones are ovoid, 5-8 cm long and 3-4 cm broad, with thin, scales. The cones mature in autumn, about 18 months after pollination, and open to release the seeds.
Red pine is a widely planted timber tree in North America. The wood is strong and durable, and is used for construction, pulp, and lumber. The tree is also an important source of wildlife food and shelter.
What is the yellow stuff in Crater Lake?
Pine pollen is a common occurrence in many lakes and is nothing to be concerned about. It is simply the pollen from pine trees that have blown into the lake.
The park’s water claim for the lake is for the preservation and protection of all natural habitats and the conservation of scenery. It is not for human consumption. The lake is home to many different species of wildlife and plants, and is an important part of the park’s ecosystem. By protecting the lake’s water, the park is able to maintain its natural beauty and ensure that its wildlife and plant life remain healthy and thriving.
Why can’t you swim in Crater Lake?
Crater Lake is one of the snowiest places in America, with an average of 43 feet of snow per year. As a result, there are only a few months when people can swim at Crater Lake, usually from June through September.
A freshwater crocodile lives in Lake Eacham. Unlike estuarine crocodiles, freshwater crocodiles are considered timid and non life-threatening to humans. Very few incidents have been reported involving people.
What is the danger in Crater Lake
Volcano hazards at Crater Lake fall into two main categories: 1) eruptions within the caldera, reflecting reawakening of the Mazama system, where Crater Lake itself will play an important role in determining the hazardous potential, and 2) eruptions from new vents on the flanks or in the surrounding region.
Eruptions within the caldera have the potential to be the most hazardous, due to the close proximity of Crater Lake to potential vents. If an eruption were to occur, the lake could be disrupted, causing waves and flooding. In addition, the eruption could itself be hazardous, with lava, ash, and gases potentially causing harm to people and property.
Eruptions from new vents on the flanks or in the surrounding region could also be hazardous. If the eruption is large enough, it could disrupt the caldera, causing Crater Lake to overflow. Additionally, lava, ash, and gases from the eruption could cause harm to people and property downwind of the volcano.
Crater Lake, Oregon is an absolutely stunning place. The water is so clean and clear, and the views are incredible. It’s definitely worth a visit!
Are there any fish in Crater Lake?
Between 1888 and 1941, the lake was stocked with seven different species of fish. Of those species, only two thrive today. The lake is currently estimated to support approximately 60,000 kokanee salmon and rainbow trout.
Crater Lake National Park is one of the most beautiful places on Earth. The lake is so clear because it is filled almost entirely by snowfall. The park is also home to many different kinds of animals, including some of the world’s rarest species.
Is redwood tree same as the pine tree
A sequoia is not a pine tree at all! Sequoiadendron giganteum is also called Sierra redwood, a coniferous evergreen tree of the cypress family (Cupressaceae), the largest of all trees in bulk and the most massive living things by volume.
Different families of trees produce different types of cones. Members of the pine family (pine, spruce, fir and cedar) have cones with overlapping scales. Members of the cypress family (cypress, juniper and redwoods) have cones with scales that are completely fused.
What is the 2 needle pine tree?
There are four species of pine trees that are similar in many ways but have some key differences. The Scots pine, Austrian pine, red pine and Jack pine all have needles in bundles of two. The Scots pine needles are the only ones that are twisted. The Austrian pine and red pine needles are the longest, and Jack pine needles are widely spread like a jumping jack.
The common garter snake is a species of snake that is found in North America. It grows to a length of 3 feet and is black in color. This snake is known to be found in the caldera of Crater Lake and is believed to have evolved as a result of protective coloration against the black volcanic rocks.
Warp Up
There are a variety of trees at Crater Lake, including Douglas fir, sugar pine, whitebark pine, red fir, mountain hemlock, and true fir.
The trees at crater lake are mostly coniferous, with a few deciduous trees mixed in. The most common coniferous trees are Douglas fir, ponderosa pine, and lodgepole pine. The deciduous trees include quaking aspen and paper birch. All of these trees are native to the area.